Here’s what you’ll find in this week’s AI update:
- OpenAI sued over data privacy & copyright violation claims
- Google updates privacy policy to allow data scraping for AI training
- ChatGPT’s Browse with Bing disabled over paywalled content concerns
- 150+ EU Companies sign open letter cautioning over-regulation of AI in the EU
- NYC’s Bias Audit Law comes into effect.
OPENAI SUED OVER DATA PRIVACY & COPYRIGHT VIOLATION CLAIMS

On June 28, two lawsuits were filed against OpenAI in the U.S. California District Court.
First, a class-action lawsuit which alleges that OpenAI unlawfully scraped datasets containing sensitive personal information (including medical data, private conversations, and even data of minors) to train its AI models – ChatGPT and Dall-E, in violation of the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act, 1986 (CFAA).
Second, a copyright infringement suit filed by two authors claiming unauthorized use of their books to train the GPT 3.5 and GPT 4 models. The lawsuit alleges that OpenAI’s training datasets include copyrighted works sourced from illegal “shadow libraries” which violate the provisions of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act, 1998 (DMCA).
GOOGLE UPDATES PRIVACY POLICY TO ALLOW DATA SCRAPING FOR AI TRAINING

On July 1, Google updated its privacy policy, clarifying that the company may use publicly available data for AI training. This policy revision by Google follows closely on the heels of OpenAI, which is being sued for data privacy and copyright infringement claims.
CHATGPT’S BROWSE WITH BING DISABLED OVER PAYWALLED CONTENT CONCERNS
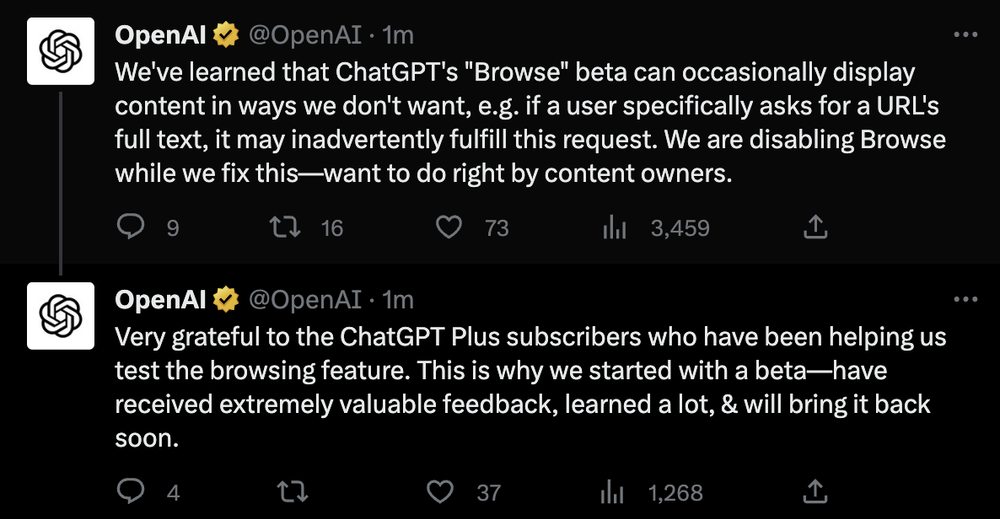
On July 3, OpenAI disabled ChatGPT’s Browse with Bing beta feature (available only to ChatGPT Plus subscribers) which allows access to the internet to help answer user questions, after reports claimed that it displayed information from paywalled websites.
150+ EU COMPANIES SIGN OPEN LETTER CAUTIONING OVER-REGULATION OF AI IN THE EU
On June 30, stakeholders from 150 companies in the EU, including significant-tech founders, CEOs, VCs, and industry giants like Airbus, Felix Capital, Heineken, Renault, and Siemens, demonstrated collective action by writing an open letter to the European Parliament, Commission, and member states. The letter warned that excessive regulation of AI in the proposed EU AI Act could cause innovative companies to seek investment opportunities abroad, and impose disproportionate compliance and liability costs on companies developing AI systems.
NYC BIAS AUDIT LAW COMES INTO EFFECT

On July 5, New York City’s Local Law 144 (also referred to as Bias Audit Law), which regulates automated employment decision tools (AEDTs) was brought into effect. It requires hiring organizations to inform job applicants that algorithms that automate the process are being used, and conduct independent software risk assessments. California, Illinois, Maryland, and Washington, also have or are considering regulating AEDTs.
Authors: Shantanu Mukherjee, Anushka Iyer, and Vishnu Rao.