Here’s what you’ll find in this week’s AI update:
- UK Parliamentary Committee releases report on AI
- Delhi High Court holds that ChatGPT responses cannot be used as evidence
- US Copyright Office issues Notice of Inquiry on Generative AI
- Google develops digital watermark to identify AI-generated images
- US Air Force program introduces next-gen AI drone
UK PARLIAMENTARY COMMITTEE RELEASES REPORT ON AI
On 31 August, 2023, the UK House of Commons Science, Innovation, and Technology Committee published a report titled “The governance of artificial intelligence: interim report” with recommendations, urging the government to respond within 2 months in order to develop a regulatory framework for AI ahead of the Global AI Safety Summit in November. The report lays down 12 challenges of AI policymaking which has to be addressed by the legislators which includes the challenges of bias, privacy, misrepresentation, access to data, intellectual property rights, liability, amongst others.
DELHI HIGH COURT HOLDS THAT CHATGPT RESPONSES CANNOT BE USED AS EVIDENCE

On 22 August, 2023, the Delhi High Court heard a case wherein the counsel of the plaintiff tried to establish the reputation and goodwill of the brand by submitting a response generated by ChatGPT affirming its reputation. The case in question before the Delhi High Court involved a lawsuit instituted by luxury fashion designer Christian Louboutin against a partnership firm that manufactured shoes, alleging violation of trademark. In a judgement penned by Justice Prathiba Singh, the Delhi High Court recognized that the accuracy and reliability of AI generated data is still nascent and cannot substitute the human element in the adjudicatory process. While the court acknowledged that AI tools may be used for preliminary research, it also opined that AI generated data cannot be the basis for deciding legal or factual issues due to its limitations.
US COPYRIGHT OFFICE ISSUES NOTICE OF INQUIRY ON GENERATIVE AI
The US Copyright Office issued a Notice of Inquiry on August 30, 2023 seeking public comment on copyright law-related issues raised by the rapid development of generative AI systems. The issues raised includes the use of copyrighted works to train AI models, a problem raised primarily by news and media agencies. The other areas of policy that the Copyright Office is looking into is the copyrightability of AI-generated material, treatment of AI-generated outputs that mimic human artists and the liability in case of AI-generated material that is infringing other copyright protected works.
OPENAI INTRODUCES CHATGPT ENTERPRISE
On August 28, 2023, OpenAI introduced the most powerful version of ChatGPT yet, “ChatGPT Enterprise”. This version of ChatGPT offers enterprise-grade security, unlimited access to GPT-4, longer context windows for processing longer inputs, and several other features. The most important feature, however, is a higher level of data protection, as ChatGPT Enterprise offers its users complete control over their data. OpenAI does not use business data or conversations to train their model, and the models do not learn from the usage of ChatGPT Enterprise. Several companies including Block, Canva, Carlyle, The Estée Lauder Companies, PwC, and Zapier are already integrating ChatGPT Enterprise into their businesses to streamline communication, coding, business tasks etc.
GOOGLE DEVELOPS DIGITAL WATERMARK TO IDENTIFY AI-GENERATED IMAGES

DeepMind, an artificial intelligence research laboratory that is a wholly owned subsidiary of Google, has developed a digital watermark named SynthID to help identify images generated by AI. SynthID is effectively an invisible watermark as it reflects in individual pixels of images, making it imperceptible to the naked eye but identifiable by computers. This move follows the commitment undertaken in July by 7 leading technology companies, including Google, to manage the risks of AI, and intends to fight misinformation and deepfakes as AI image generators become more mainstream and evolved.
US AIR FORCE PROGRAM INTRODUCES NEXT-GEN AI DRONE
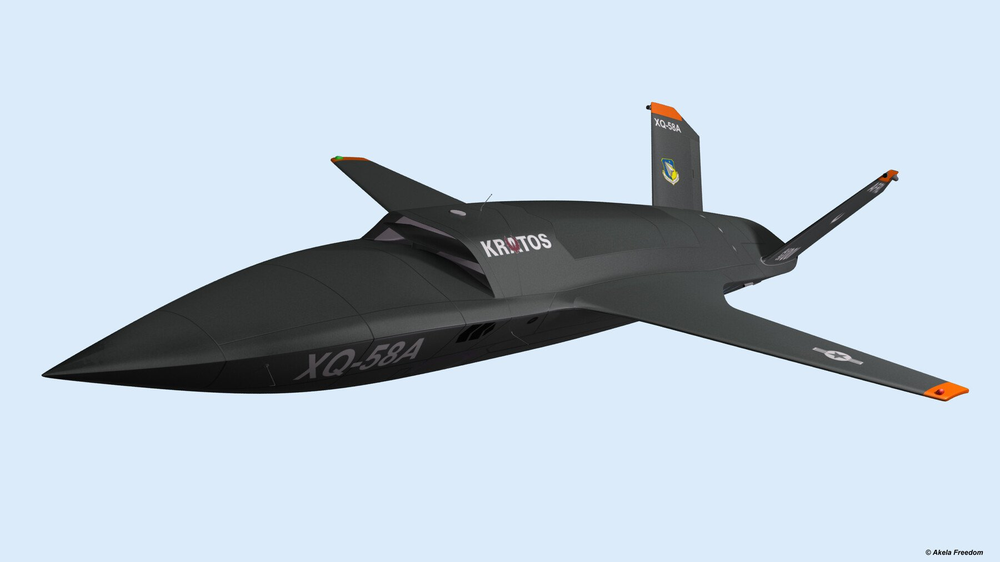

The US Air Force’s pilotless XQ-58A Valkyrie experimental aircraft is run by artificial intelligence. The Valkyrie is designed to supplement traditional fighter jets and act on human directions to identify, evaluate and eliminate threats. The Air Force plans to build a critical mass of these AI drones with a range of specialized types to serve various purposes. However, this move has resurfaced concerns about the military use of artificial intelligence, especially by human rights agencies who are pushing for restrictions on autonomous weapons.
Authors: Hena Ayisha, Shruti Gupta, and Anushka Iyer